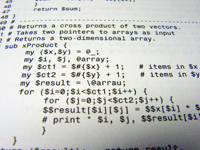
|
The best way to explain XQuery is to say that XQuery is to XML what SQL is to
database tables.
XQuery is designed to query XML data - not just XML files, but anything that can
appear as XML, including databases.
What You Should Already Know
Before you continue you should have a basic understanding of the following:
-
HTML / XHTML
-
XML / XML Namespaces
-
XPath
If you want to study these subjects first, find the tutorials on our
Home page.
What is XQuery?
-
XQuery is the
language for querying XML data
-
XQuery for XML is like SQL for databases
-
XQuery is built on XPath expressions
-
XQuery is defined by the W3C
-
XQuery is supported by all the major database engines (IBM, Oracle, Microsoft,
etc.)
-
XQuery will become a W3C standard - and developers can be sure that the code
will work among different products
XQuery is About Querying XML
XQuery is a language for finding and extracting elements and attributes from XML
documents.
Here is an example of a question that XQuery could solve:
"Select all CD records with a price less than $10 from the CD collection stored
in the XML document called cd_catalog.xml"
XQuery and XPath
XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 share the same data model and support the same
functions and operators. If you have already studied XPath you will have no
problems with understanding XQuery.
You can read more about XPath in our
XPath Tutorial.
XQuery - Examples of Use
XQuery can be used to:
-
Extract information to use in a Web Service
-
Generate summary reports
-
Transform XML data to XHTML
-
Search Web documents for relevant information
XQuery is Not (Yet) a Web Standard
XQuery is compatible with several W3C standards, such as XML, Namespaces, XSLT,
XPath, and XML Schema.
However, XQuery 1.0 is not yet a W3C Recommendation (XQuery is a Working Draft).
Hopefully it will be a recommendation in the near future.
To read more about the XQuery activity at W3C, please read our
W3C Tutorial.
|